- What are the Basic Rights of GDPR?
- The right to access
- The right to be forgotten
- The right to data portability
- The right to be informed
- The right to have the information corrected
- The right to restrict processing
- The right to object
- The right to be notified
- What falls under GDPR compliance?
- How to get ready for GDPR compliance?
- What are the organizational impacts of GDPR compliance?
- How can Elsner help you?
Introduction to GDPR Compliance:
GDPR is a series of rules intended to provide EU or UK people more control over their private information. It aspires to simplify corporate regulations so citizens and businesses can fully benefit from the digital economy.
The GDPR law defines personal data as any information that identifies a specific individual, including name, photograph, email address, bank information, updates on social networking websites, location information, medical data, and computer IP address.
The same personal information represents the same person, whether acting in a private, public, or professional capacity. In IT, communication and knowledge exchange between and among individuals is crucial to everything. Businesses serve as customers, but interactions that deal with business-related concerns occur between persons or individuals.
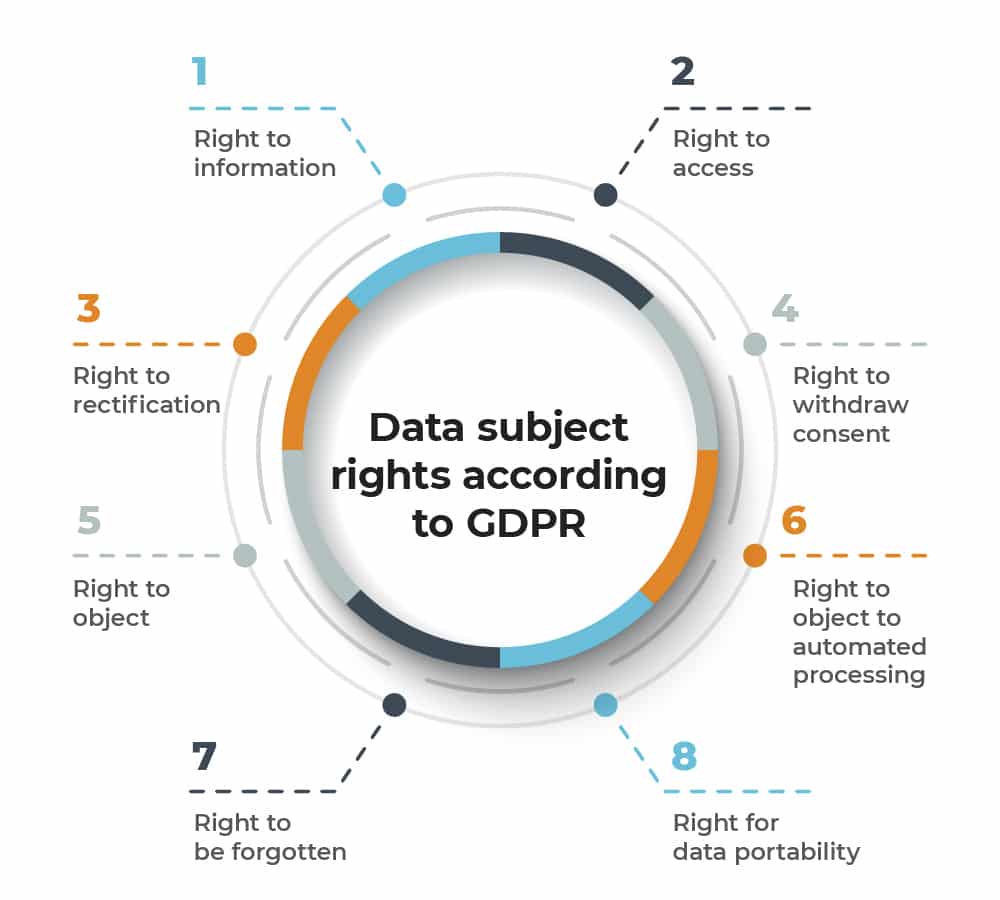
What are the Basic Rights of GDPR?
Under the GDPR, individuals have:
 [Image Source: https://bit.ly/3ryMEBn]
[Image Source: https://bit.ly/3ryMEBn]
The right to access
It means that individuals have the authority to ask for access to their data and information about how the business uses their data once it has been collected. The business must give customers a free electronic copy of their personal data upon request.
The right to be forgotten
Consumers can request that their data be destroyed if they stop being customers or withdraw their consent for a corporation to use their data.
The right to data portability
People are entitled to move their data from one service provider to another. And it needs to be done in a format that is both generally used and machine-readable.
The right to be informed
It refers to any data collection by businesses that must inform people before data collection. This consumer process requires consent, which must be expressly supplied rather than implicit.
The right to have the information corrected
It guarantees that users can get their data updated if it is outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate.
The right to restrict processing
People have the option to request that their data not be processed. Their record may still exist, but they will not use them.
The right to object
It includes individuals with the right to stop having their data processed for direct marketing purposes. There are no exceptions to this rule, and processing must cease immediately upon receipt of the request. Additionally, individuals must be aware of this at the outset of any contact.
The right to be notified
An individual has a right to be informed within 72 hours of first becoming aware of a data breach that exposes their personal information.
What falls under GDPR compliance?
- Business Legal Teams, Legal advisers, data protection officers (CISO), and information security teams must be advised and involved in various strategies relating to privacy, compliances, controls, draught clauses inclusions, consents, data storage, etc., increasing the involvement of Board executives.
- Companies that do not comply will be placed in one of two categories; the higher category could cost the company up to €20 million or 4% of its global annual revenue, whichever is higher.
- Along with a proactive attitude, accountability transparency is necessary.
- Disclaimers, Terms and Conditions, Privacy Notices, and Consent must all be clearly stated.
- In case of any data breach, notify the relevant data protection authorities within 72 hours of becoming aware.
- There must be options for access, alteration, rectification, and cleansing, among other things.
- It is necessary to explicitly identify data controllers and processors through contractual procedures and receive written confirmation from each.
There should be data portability and, if applicable, disclosures to third nations. - Pseudonymization and data minimization are to be used to the fullest extent practicable.
- Data set categorization, especially when it contains sensitive information like health, finances, etc.
How to get ready for GDPR compliance?
- Map your company’s data: Map the sources of all the personal data used by your entire company and keep track of what you do with it. Determine the location of the data, who has access to it, and whether the data is at risk. Additionally to being crucial for GDPR, this will enhance customer relationship management.
- Determine what data you need to keep: Keep only the information you need, and delete any information you aren’t using. Consider which data is crucial to your company currently if your company has gathered a lot of data without any meaningful usefulness. The GDPR promotes more systematic handling of personal data.
- Put security measures in place: Create and execute security measures across your infrastructure to help stop data breaches. This entails putting security measures in place to prevent data breaches and acting quickly to alert people and authorities if a breach does happen.
- Review your documentation: Individuals must expressly consent to collecting and processing their data under GDPR. Implied consent and pre-checked items will no longer be accepted. All your privacy disclosures and statements will need to be reviewed, and any necessary changes made.
- Create guidelines for managing personal data: As mentioned above, the GDPR grants every person eight fundamental rights. You must now design policies and procedures to address each of these scenarios.
What are the organizational impacts of GDPR compliance?
- Benefits of GDPR compliance include improved trust, credibility, and knowledge of the data being gathered and how it is managed.
- Due to the implementation of GDPR, it is now mandatory for several businesses to hire a DPO, CISO, internal information security staff, and external data auditors.
- According to estimates, 30,000 new DPOs will be needed in Europe alone. Organizations will be subject to the largest penalty if the GDPR is not followed, which may be up to 4% global turnover.
- The concept of ”Privacy By Design” is already codified in legislation. Over the next few years, the Privacy Impact Assessment is anticipated to become a standard practice across all companies.
- Organizations must adjust encryption methods, masking techniques, pseudonymization, and data minimization as and when necessary by changing local legislation.
How can Elsner help you?
We understand that a client needs a GDPR audit to ascertain if the firm has put in place good policies and procedures to control the processing of personal data. Additionally, the evaluation will ensure that such policies and practices will monitor the processing of personal data to identify and manage risks to prevent data breaches.
Our team of highly skilled and knowledgeable lawyers adds a new dimension to advisory services with benchmarked ethical standards and professionalism.
We will help you to make your businesses compliant with data protection regulations and create an ecosystem with data protection and subject data security as its core.
Conclusion
It is crucial to achieving GDPR compliance. Elsner can assist you if you want to keep customers satisfied, avoid paying fines and see your business flourish. Our solutions eliminate data loss, protect data from unauthorized access, and shield your information from breaches so you won’t have to worry.

About Author
Pankaj Sakariya - Delivery Manager
Pankaj is a results-driven professional with a track record of successfully managing high-impact projects. His ability to balance client expectations with operational excellence makes him an invaluable asset. Pankaj is committed to ensuring smooth delivery and exceeding client expectations, with a strong focus on quality and team collaboration.